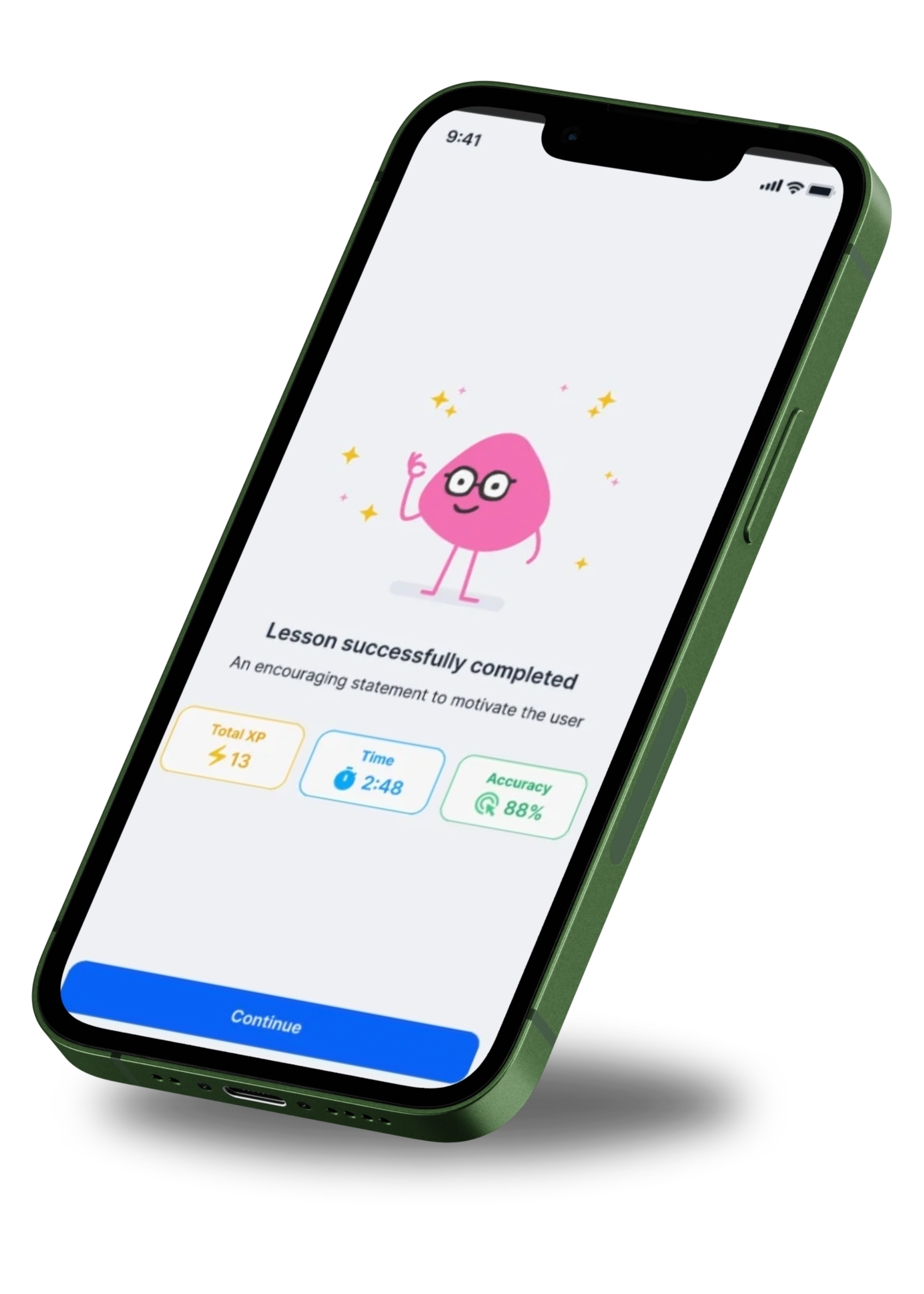
ANAP Microcredential Curriculum Overview
This page lists the full CRNA CE catalog available in Ollivate.
ANAP learning content is organized by category and topic to help registered nurses explore core anesthesia concepts and build familiarity with material commonly encountered in CRNA training.
ANAP is a preparatory, optional microcredential for registered nurses and does not replace formal CRNA program coursework or clinical education.
Scroll for more info ↓
-
Understand what anesthesia is, its goals, and how it supports patient safety and comfort during surgical and procedural care.
-
Learn the differences between general, regional, monitored anesthesia care, and local anesthesia, and when each is used.
-
Identify the roles and responsibilities of professionals involved in anesthesia care and how the team works together.
-
Review the typical perioperative workflow from preoperative assessment through recovery and postoperative care.
-
Understand the principles of patient safety, vigilance, and accountability that define nurse anesthesia practice.
Module 1: Introducing the World of Anesthesia
This module establishes a broad understanding of anesthesia care and the perioperative environment, helping learners orient themselves to the clinical, team-based, and safety-driven nature of nurse anesthesia practice.
Module 2: Mastering the Basics: Airway Assessment and Management
Focuses on foundational airway knowledge and assessment skills essential to safe anesthesia care, emphasizing anatomy, equipment, and basic management techniques.
-
Understand upper and lower airway anatomy and the physiologic principles that support ventilation and oxygenation.
-
Learn how to evaluate the airway and identify features that may predict difficulty with ventilation or intubation.
-
Identify commonly used airway devices and understand their basic function and clinical use.
-
Understand the fundamentals of airway management techniques used to support ventilation and secure the airway.
-
Learn core concepts of oxygen delivery, preoxygenation, and safe intubation practices.
-
Understand how capnography and pulse oximetry monitor ventilation and oxygenation during anesthesia care.
Module 3: Cardiovascular Foundations for Anesthesia
Introduces key cardiovascular concepts relevant to anesthesia, helping learners understand hemodynamics, monitoring, and common perioperative medications.
-
Understand basic cardiac anatomy and physiology, including heart function, cardiac output, and circulation.
-
Learn what determines blood pressure, how it is measured, and why it matters during anesthesia care.
-
Recognize basic EKG components and common rhythms relevant to perioperative monitoring.
-
Identify commonly used cardiovascular medications in the operating room and their primary effects on heart rate and blood pressure.
Module 4: Pharmacology Foundations for Nurse Anesthesia
Provides a foundational overview of anesthesia-related pharmacology, focusing on how drugs work, interact, and are used safely in clinical settings.
-
Understand how drugs move through the body and produce effects at target sites.
-
Learn basic receptor theory, including agonists, antagonists, and receptor affinity.
-
Identify induction agents, opioids, muscle relaxants, and their primary purposes during anesthesia care.
-
Recognize commonly used reversal agents and emergency medications and understand when and why they are administered.
-
Understand drug interactions and patient-specific factors that influence medication selection and safety.
Module 5: Introduction to Anesthesia Machines and Monitoring
Introduces essential anesthesia equipment and monitoring systems, highlighting how technology supports safe anesthetic delivery and patient assessment.
-
Understand the purpose and core components of the anesthesia machine.
-
Learn how medical gases are delivered and how vaporizers administer inhaled anesthetic agents.
-
Understand how breathing circuits function and how CO₂ absorbers allow safe rebreathing.
-
Recognize common anesthesia machine alarms and the conditions they indicate.
-
Understand essential anesthesia monitors, including EKG, NIBP, EtCO₂, temperature, and neuromuscular monitoring.
Module 6: The Perioperative Journey: From Assessment to Recovery
This module follows the patient through the perioperative continuum, emphasizing safety, communication, and coordinated care before, during, and after anesthesia.
-
Understand airway evaluation, ASA classification, and allergy review as part of preoperative preparation.
-
Recognize the importance of positioning, thermoregulation, and safety checks during surgery.
-
Understand PACU priorities, discharge criteria, pain management, and PONV considerations.
-
Learn how accurate documentation and effective communication support continuity of care.
Module 7: Anesthesia Considerations for Special Populations
Explores how patient-specific factors influence anesthesia planning, risk, and management across diverse populations.
-
Understand physiologic differences, airway considerations, and drug dosing in pediatric patients.
-
Recognize key intraoperative priorities that support patient safety, including positioning, temperature
management, and standardized safety checks.
-
Learn how frailty, pharmacokinetic changes, and cognitive risk affect anesthesia care in older adults.
-
Understand how obesity impacts airway management, drug dosing, and respiratory function.
Module 8: Anesthesia Emergencies: Recognition, Response, and Prevention
Introduces common anesthesia-related emergencies, focusing on early recognition, initial response, and patient safety.
-
Recognize early signs of malignant hyperthermia and understand immediate response priorities.
-
Identify signs of perioperative anaphylaxis and initial management strategies.
-
Recognize hypotension, bradycardia, and tachyarrhythmias and understand basic response strategies.
-
Understand risk factors and strategies to reduce perioperative nausea, vomiting, and aspiration.
-
Recognize how equipment issues and human factors contribute to anesthesia-related events.
Module 9: Becoming a CRNA: The Roadmap to Advanced Practice
An overview of the nurse anesthesia career pathway, offering insight into education, training, and professional expectations.
-
Understand prerequisites, education requirements, and clinical experience needed to pursue nurse anesthesia.
-
Review curriculum structure, clinical training, and academic demands of CRNA programs.
-
Explore CRNA scope of practice, autonomy, and impact on patient care.
-
Learn key components of CRNA program applications, timelines, and preparation strategies.
-
Understand what CRNA programs assess during interviews and how candidates can prepare.